Blood Tests & Testing at home
- July 30,2024
- 8 Min Read
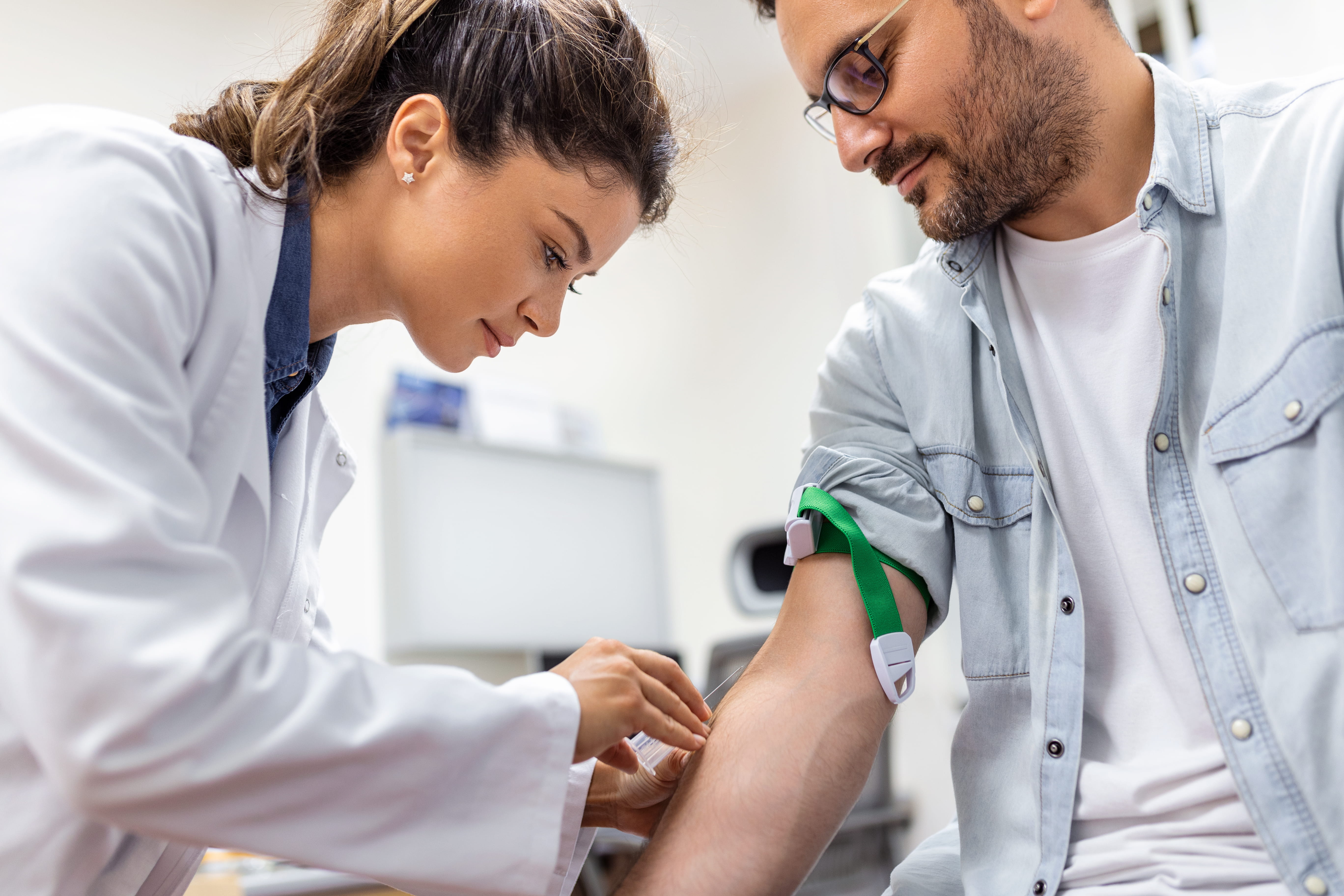
Blood Tests:
Blood tests, a cornerstone of medical diagnostics, entail the analysis of cells, chemicals, proteins, and other substances present in the blood. This type of testing, commonly referred to as blood work, is extensively employed for various purposes:
- Diagnosis: Blood tests aid in identifying numerous diseases and conditions.
- Monitoring: They play a crucial role in tracking chronic diseases like diabetes or high cholesterol.
- Treatment Assessment: Blood tests help assess the efficacy of treatments administered for various conditions.
- Organ Function Evaluation: They provide insights into the functionality of vital organs such as the liver, kidneys, heart, and thyroid.
- Detection of Bleeding or Clotting Disorders: Blood tests are instrumental in diagnosing disorders related to bleeding or clotting.
- Immune System Assessment: They assist in gauging the immune system's ability to combat infections effectively.
Types of Blood Test:
1) CBC: A complete blood count (CBC) is a comprehensive blood test that assesses various components and characteristics of your blood, including:
- Red blood cells, responsible for transporting oxygen from the lungs to the body.
- White blood cells are the body's frontline warriors, fighting off infections and diseases to keep us healthy.
- There are five primary types of white blood cells, and a CBC measures their total count. A CBC with differential, on the other hand, quantifies each type individually.
- Platelets, essential for blood clotting and preventing excessive bleeding.
- Hemoglobin: the key protein in red blood cells, transporting oxygen throughout the body.
- Hematocrit, indicating the proportion of blood composed of red blood cells.
- Mean corpuscular volume (MCV), providing insight into the average size of red blood cells.
- A CBC is also known by other names such as full blood count or blood cell count.
2) Basal Metabolic Panel: A basic metabolic panel (BMP) is a blood test that analyses eight key substances in your bloodstream. This panel offers valuable insights into your body's chemical equilibrium and metabolic processes, which govern how your body converts food into energy.
- A basic metabolic panel evaluates several crucial substances in your blood, including:
- Glucose: This sugar serves as a primary energy source for your body and brain, also known as blood sugar. Elevated levels may indicate diabetes.
- Calcium: Essential for nerve, muscle, and heart function, as well as blood clotting, calcium is a vital mineral found in bones and blood.
- Blood urea nitrogen (BUN): Reflects the levels of urea, a waste product eliminated by the kidneys.
- Creatinine: A byproduct of muscle metabolism, creatinine is filtered out of the blood by the kidneys.
- Electrolytes: These minerals, which carry electric charges when dissolved in fluid, are crucial for nerve, muscle, and pH balance regulation:
- Sodium: Regulated by the kidneys, sodium comes primarily from diet and plays a role in various bodily functions.
- Potassium: Present in body tissues and obtained from food, potassium is vital for cell function.
- Bicarbonate: Indicates blood carbon dioxide levels and helps maintain pH balance.
- Chloride: Works in conjunction with other electrolytes to regulate bodily processes.
3) Blood Clotting Test: A coagulation panel evaluates the clotting function of your blood, assessing both the speed and effectiveness of clot formation. While clotting is essential for wound healing, abnormal clotting in veins or arteries can pose severe health risks. This panel enables doctors to gauge your overall health and identify underlying conditions that may impact clotting. Results from a coagulation panel are instrumental in diagnosing various conditions, including:
- Acute myeloid leukemia
- Hemophilia (characterized by excessive bleeding tendencies)
- Liver disorders affecting clotting factors
- Thrombosis (abnormal blood clot formation)
- Vitamin K deficiency, which can impair proper blood clotting
4) C Reactive Protein (CRP): CRP (C-reactive protein) is produced by the liver in response to inflammation in the body's tissues. Elevated CRP levels, as indicated by a CRP test, may signal inflammation stemming from various sources, including:
- Artery inflammation
- Cancer
- Heart disease
- Infections
- Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)
- Lupus
- Rheumatoid arthritis
5) Enzyme Marker Test: An enzyme marker blood test quantifies the concentrations of particular enzymes in your bloodstream. When musculoskeletal disorders, organ damage, or injuries occur, enzymes may escape from cells into the bloodstream, leading to detectable levels in the blood.
Pre requisite for a blood test:
Before a blood test, your doctor will provide guidance on any necessary preparations. This may include:
- Fasting: You might need to refrain from eating or drinking anything except water for a specific duration before certain tests.
- Medication adjustments: They may advise you to temporarily discontinue certain medications, like anticoagulants, to ensure accurate test results.
What happens at a blood test?
During a blood test, typically conducted at a hospital/diagnostic centre, the process usually lasts around 10 minutes.
- A healthcare professional will draw a small blood sample, usually from the inner elbow, using a needle. In some cases, blood may be drawn from the wrist or obtained via a finger-prick test.
- To facilitate blood collection, a soft strap called a tourniquet may be placed around your arm.
- You may feel a slight scratch as the needle is inserted, which could cause mild discomfort. The collected blood is transferred into a small tube and sent to a laboratory for analysis.
- After the procedure, you'll receive cotton wool or a plaster to cover the puncture site.
- Some bruising or swelling around the area where blood was drawn may occur, but it typically resolves within a few days.
How to do a home blood test at home?
At Suburban Diagnostics, we prioritize patient comfort and convenience by offering home visits when necessary. Our dedicated team, equipped with medical expertise and training, ensures reliable blood collection at the patient's preferred location, be it their home or office. Throughout every procedure, we uphold the highest standards of healthcare practices, fostering trust and confidence among patients, doctors, and family members alike.
How to book an appointment at Suburban Diagnostics?
Scheduling a blood test is hassle-free and can be initiated either by the patient directly or through our office.
Booking an appointment is straightforward:
- Contact our health line or fill out an online form to schedule an appointment.
- Provide essential details such as name, address, telephone number, and the specific tests needed.
- Based on the provided information, we'll guide patients on any necessary preparations, such as fasting for certain tests.
Upon confirmation of the test date and time:
Our skilled technician will promptly visit the patient's location to collect the blood sample, ensuring secure transportation to our laboratory for processing.
For your convenience, you can choose how to receive the test results:
- Receive results via email.
- Have them sent to your clinic.
- Conveniently download them online from our website.
FAQ’s
Why blood tests?
Understanding the essence of a blood test is pivotal before delving into its significance. Essentially, a blood test entails the analysis of substances present in your blood, encompassing cells, proteins, and other vital components.Blood tests serve multifaceted purposes:
- Evaluate overall health status.
- Detect infections or abnormalities.
- Assess organ functionality.
- Screen for genetic diseases or disorders.
- Evaluate blood clotting factors.
- Facilitate early diagnosis of potential health conditions.
- Determine individual risk profiles for specific conditions.
- Identify variations in hemoglobin, such as hemoglobin S, C, and E.
- Monitor disease progression.
- Assess treatment effectiveness.
What are the advantages of home blood tests?
In today's fast-paced world, every minute holds significance. At-home blood testing eliminates the need for travel and saves precious time while ensuring the same quality and benefits as blood sampling at a service centre.
Which test needs to be done every year to keep a track of your health?
A complete blood count (CBC) is a routine blood test conducted during annual physicals, offering a comprehensive overview of your blood composition. It assesses various components such as red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, hemoglobin, and hematocrit. Deviations from normal levels can indicate potential issues related to bone marrow function, immune system health, or exposure to viruses or environmental factors.
What are the key components affecting blood routine examination?
A standard blood routine exam comprises various components, each offering valuable insights into your health:
- Red Blood Cell Levels: Responsible for oxygen transportation, abnormal RBC levels may indicate issues such as dehydration, anaemia, or bleeding. Normal ranges vary by gender.
- White Blood Cell Levels: Essential for fighting infections and diseases, deviations from normal WBC levels may signal infection, blood cancer, or immune system disorders.
- Platelet Levels: Crucial for blood clotting, abnormal platelet levels could indicate clotting or bleeding disorders.
- Haemoglobin Levels: Found in RBCs, abnormal haemoglobin levels may suggest conditions like anaemia, sickle cell disease, or thalassemia.
- Haematocrit Levels: Measures the percentage of blood occupied by RBCs. Elevated levels may indicate dehydration, while low levels may suggest anaemia.
- Mean Corpuscular Volume (MCV): Measures the average size of RBCs. Abnormally low MCV levels may indicate anaemia or thalassemia.
- These components provide valuable information about your overall health and can help diagnose and manage various conditions.
Want to book a test? Fill up the details & get a callback
Most Viewed
Premarital Health Screening
- 20 Min Read
Typhoid - Signs and Symptoms
- 3 Min Read
Home Isolation Guidelines - Covid-19 Care
- 5 Min Read
HLA B27 Detection: Flow Cytometry & PCR
- 1 Min Read