Fatty Liver Disease: Symptoms and Causes
- March 14,2022
- 2 Min Read
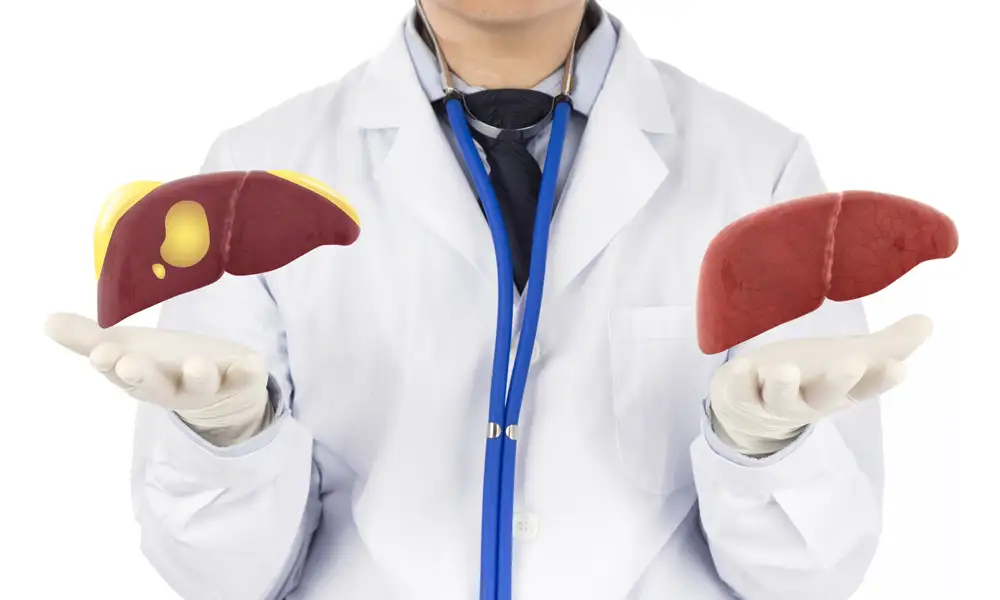

What is a Fatty Liver Disease?
Fatty liver disease (Steatosis) is a common condition caused by having too much fat build up in your liver. In most cases, the fatty liver disease doesn’t cause any serious problems, but for up to 30% of people, the fatty liver disease gets worse over time. In these people, it progresses through three stages:
-
Liver becomes inflamed (swollen), which damages its tissues. This stage is called Steatohepatitis.
-
Scar tissue forms where your liver is damaged. This process is called Fibrosis.
-
Extensive scar tissue replaces healthy tissue. At this point, you have Cirrhosis of the liver.
Types of Fatty Liver disease:
-
Alcoholic liver disease
-
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
People who are at risk include:
-
For alcoholic fatty liver:
-
Those who consume alcohol in excess
-
-
For non-alcoholic fatty liver:
Individuals with one or more of the following conditions are at a higher risk for developing non-alcoholic fatty liver.
-
Obesity
-
Type 2 diabetes
-
High triglyceride / low HDL
-
Older age
-
PCOS
-
Hyperthyroidism
-
Metabolic syndrome (combination of diabetes, high blood pressure and obesity)
Reversing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD):
There is a fat build-up in your liver, but unlike other liver diseases, there is no damage to the organ, initially. There are steps you can take to rewind to a healthy liver in case of a Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver:
-
Lose weight, exercise and be mindful of your diet
-
Eat high-fiber food
-
Reduce carbohydrates and say no to sugar
-
Limit your consumption of Saturated and Trans fats
-
Reduce salt from your diet. Packaged food contains high amounts of salt, avoid them as much as possible. Go for more healthier snacks like fruits, or healthier alternatives.
-
You might have other conditions like diabetes, high cholesterol, high triglycerides, etc. which might be linked to your liver condition. Treating them might also improve the health of your liver.
Source: https://www.webmd.com/digestive-disorders/reverse-nonalcoholic-fatty-liver-disease
Signs and Symptoms of Fatty Liver:
It often has no symptoms. But if the disease progresses to fibrosis or cirrhosis, fatty liver causes:
-
Abdominal pain or a feeling of fullness
-
Nausea, loss of appetite or weight loss
-
Yellowish skin and whites of the eyes (jaundice)
-
Swollen abdomen and legs (edema)
-
Extreme tiredness or mental confusion
-
Weakness
How to check for Fatty Liver:
Fatty liver can be detected primarily through the use of-
Radiology tests: Ultrasounds, CT scans and MRI can all be used to detect fatty liver, though ultrasound scans are the most cost effective.
Blood tests: Liver enzymes like ALT* and AST will be elevated in case of a fatty liver. It is recommended to couple blood tests with radiology tests in order to diagnose liver disease.
Diet for reducing Fatty Liver:
Diet is a big part of our lifestyle choices. By making sure that our diet is rich in nutrition, we can prevent many disorders and diseases before they ever become a problem. Here are some food items that make a good ‘fatty liver diet’:
-
Coffee
-
Green Leafy Vegetables
-
Soy and Beans
-
Fish
-
Oatmeal
-
Turmeric
-
Nuts
-
Sunflower Seeds
-
Garlic
If the fatty liver progresses to steatohepatitis, fibrosis or cirrhosis, a liver biopsy may be needed. If detected and managed at an early stage, it’s possible to stop fatty liver disease from getting worse. If you have any of the risk factors for fatty liver, get yourself tested.
Make your health a priority.
Want to book a test? Fill up the details & get a callback
Most Viewed
Premarital Health Screening
- 20 Min Read
Typhoid - Signs and Symptoms
- 3 Min Read
Home Isolation Guidelines - Covid-19 Care
- 5 Min Read
HLA B27 Detection: Flow Cytometry & PCR
- 1 Min Read